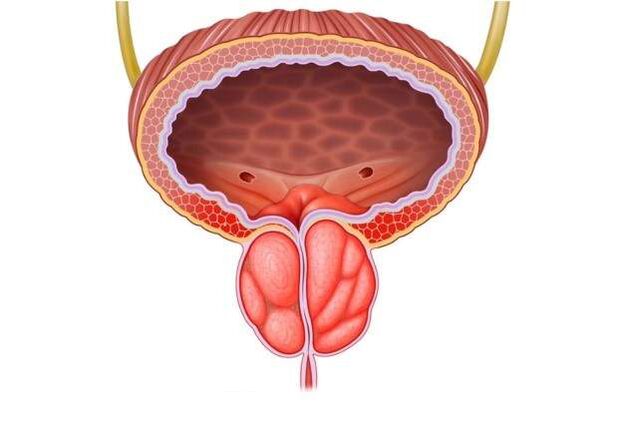
Prostatitis is a disease associated with inflammation of the prostate gland. It can develop in men of any age, wear a chronic or acute course. There are problems in diagnosis, so often patients seek help from a doctor when prostatitis is in advanced form and traditional treatment does not help. The danger lies in the high probability of developing prostate cancer and complete infertility.
If prostatitis is diagnosed in a timely manner, then the treatment lasts only 2 weeks, after which the man will only need to follow the doctor's recommendations and periodically undergo a follow-up examination. In this case, there will be no complications after the inflammation of the prostate - the reproductive abilities are preserved in full, even if the prostatitis proceeded with acute symptoms.
Prostatitis does not develop "from scratch", the cause of the onset of the inflammatory process is Escherichia coli, mycoplasmas, streptococci, staphylococci, Trichomonas and other pyogenic microorganisms. Their peculiarity lies in the very rapid reproduction and rapid destruction of prostate tissues. The main causes of the disease are:
- any inflammatory diseases of the urinary system - cystitis, pyelonephritis, urethritis;
- chronic stool disorders - in particular, constipation, in which men need to push hard and prostatitis develops as an organ response to pressure;
- infections from distant foci - severe forms of tonsillitis, pneumonia, influenza, when prostatitis is directly related to the penetration of infectious agents into the tissues of the gland;
- frequent hypothermia or, conversely, overheating - may be associated with the characteristics of labor activity;
- lack of regular sexual activity, hypodynamia - prostatitis provokes stagnation of secretion in the tissues of the prostate gland, more often it is the cause of prostatitis in a 40-year-old man;
- weakened immunity against the background of serious hormonal disorders;
- sexually transmitted infections - gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia;
- frequent urinary retention - an enlarged bladder puts strong pressure on the prostate gland;
- trauma in the pelvic area.
Most often, prostatitis develops after infection enters the prostate tissue through the urethra, much less often it occurs through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Prostatitis has one very important provoking factor - a general weakening of the immune system, if it happened as the body's response to stress, constant fatigue, nervous exhaustion, emotional "outbursts".
Men should have a regular sexual life, and their lifestyle should be made active. Otherwise, stagnation of secretion occurs in the tissues of the prostate gland, which is an ideal environment for the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms - prostatitis develops rapidly. Inevitably, prostate cells experience oxygen starvation, which only increases the chances that prostatitis will go beyond the organ - inflammation will also affect nearby organs.
Types of prostatitis in men, features of the course
Depending on the cause of origin, there are several types of prostatitis:
- bacterial prostatitis - begins against the background of penetration into the tissues of the prostate infection, the diagnosis of this type of prostatitis occurs more often in young and older men;
- congestive prostatitis - caused by a sedentary lifestyle, lack of regular sexual activity in men and injuries of the small pelvis, often accompanied by infection and then the prostatitis becomes a mixed type;
- calculous prostatitis - develops as a result of an untreated chronic form of the course of the disease, more often such prostatitis occurs in elderly men.
According to the form of the course, prostatitis is divided into acute and chronic. Diagnosis of the acute form of the disease is rare, treatment should be carried out only in a hospital, because prostatitis occurs with severe symptoms. Chronic prostatitis is characterized by a "sluggish" clinical picture, periodic remissions, a complete absence of specific symptoms and a rapid transformation into serious problems - the degeneration of healthy prostate cells into malignant ones, the cessation of secretion production, and a decrease in sperm secretion.
Symptoms and diagnosis of inflammation of the prostate gland
Symptoms directly depend on what type of prostatitis begins to develop in the tissues of the prostate gland:
- bacterial prostatitis - high body temperature, the presence of blood or pus in the urine, problems with urination (thin and weak stream, "drip" urine output), acute pain in the perineum, poor general health;
- calculous prostatitis - a weak erection or its complete absence, blood in the urine, such symptoms of prostatitis are more often present in men 50 years of age and older;
- congestive prostatitis - discomfort in the perineum and testicles, partial or complete lack of erection, improper urination.
Prostatitis of the chronic form of the course is characterized by a "blurred" clinical picture, all the symptoms are unexpressed and can disturb periodically. But if men develop pain in the groin and testicles within 2-3 months, the overall body temperature rises, and sexual desire decreases, this means that you need to see a doctor, confirm the diagnosis of "chronic prostatitis" and undergo treatment. It is worth knowing the following nuances:
- symptoms of prostatitis in men at the age of 50 are a weakening of erection and a feeling of heaviness in the groin, but the pain syndrome may be completely absent;
- symptoms of prostatitis in men at the age of 30 are always acute and the first sign is a violation of urination: an enlarged prostate compresses the bladder and men simply cannot go to the toilet;
- symptoms of prostatitis in men at the age of 60 may be absent - at this age, prostatitis is often chronic, but a complete lack of erection may be disturbing.
The doctor will be able to prescribe effective treatment only after diagnosing the disease - prostatitis often has symptoms of other diseases of the genitourinary system. Therefore, the patient's complaints alone are not enough to make a diagnosis, the following are prescribed:
- rectal examination;
- laboratory study of prostate secretion;
- analysis for the detection / refutation of sexually transmitted infections;
- ultrasound examination of the prostate;
- organ computed tomography.
As additional examinations, ultrasound examinations of the pelvic organs and scrotum may be prescribed. It may be necessary to involve narrow specialists to exclude or confirm concomitant diseases.
Treatment - general principles, course duration
The symptoms of prostatitis in a man and his treatment are directly related, because when prescribing therapy, the doctor must first of all alleviate the general condition of the patient. In men, severe pain is often present, which means that treatment should begin with painkillers. How to treat prostatitis is determined by a urologist or andrologist, and the following medications will most often be prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and diuretics - prostatitis is manifested by a violation of the urinary process;
- antispasmodics and muscle relaxants - prostatitis is accompanied by severe pain in the groin;
- supporting the functionality of the prostate and alpha-blockers.
Is the lack of erection treated against the background of prostatitis? Yes, with such complaints, the doctor prescribes specific drugs that improve the blood supply to the penis and cleanse the vessels of the prostate gland from toxins and toxins. If the symptoms of prostatitis are detected in men aged 40, then additional drugs to restore erection will not be needed - as soon as the inflammatory process stops, all sexual abilities will be restored. But if venereal diseases (sexually transmitted infections) became the cause of prostatitis in men of 30 years old, then additional treatment and the identified infection will be necessary to restore sexual activity.
The best treatment is complex and therefore, in order to stop prostatitis as quickly as possible, you need to follow some doctor's recommendations:
- consume at least 2 liters of fluid per day - prostatitis is characterized by stagnation of the secret and it will be necessary to quickly remove it from the tissues in order to reduce the load on the organ and reduce its swelling;
- adhere to bed rest - treatment cannot be combined with physical activity, because they will irritate the organ, prostatitis will only progress, which will make the treatment long and ineffective;
- exclude from the diet spicy, sour, fatty foods, alcohol - these are also irritants, in which prostatitis will only worsen.
As soon as the signs of the disease become less pronounced, it will be necessary to restore sexual activity. Prostatitis will be cured much faster if regular drainage of the prostate gland is ensured and even a slight stagnation of secretion in its tissues is not allowed.
If drug treatment does not give positive results, prostatitis occurs in a chronic form with frequent relapses, then this is a reason to perform surgical intervention. The operation can be of two types:
- transurethral resection - the surgeon removes prostate tissue that is affected by prostatitis;
- prostatectomy - prostatitis poses a real danger to a man's life, so he is completely removed both the prostate and the seminal vesicles with adjacent tissues.
Operations are not carried out at a young age, because this can lead to complete infertility - prostatitis is treated with therapeutic methods, physiotherapy procedures can be prescribed in addition to medications. How much prostatitis will be treated depends on the stage and form of the disease, the degree of neglect. Usually the treatment lasts 2 weeks, but this figure is very average.
It is possible to cure completely prostatitis, it is only important to consult a doctor in time. Treatment should be prescribed individually, alternative methods will absolutely not help to stop prostatitis, but they can bring the moment of onset of the development of complications closer.